In my previous post - Custom Window Selection in the Forge Viewer - Part I - I started to tackle custom window selection in the Forge Viewer. Here is the second part of that series.
I was showing previously how to build a projected pyramidal shape from the selected corners on the screen in order to build our selection logic. The next step today is to implement the selection logic itself. The approach is rather straightforward: we are going to use the five planes defined by the pyramid plus the camera plane - nothing behind the camera can be logically selected - to perform a first filtering on each component bounding box in the model. If a bounding box is fully contained inside the pyramid, the component is selected, if it is fully outside, the component is not selected and finally if the bounding box intersects with the pyramid, a finer analysis is required.
First thing to do is to compute a set of oriented planes based on the pyramid faces, to be consistent we want the planes normal to always points inside the pyramid, then by computing the distance from the bounding box corners to a plane, we know instantly on which side of the plane that point is located. As soon as a corner is outside, we discard that box and early exit our loop.
Here is a screenshot representing the projected pyramid along with the plane normals which I used to visually debug the command while implementing it:

We then have to iterate through each leaf component bounding box - only leaf components own geometry in the model and therefore can be selected directly - and check whether the box is inside, outside or intersects our pyramid. In this second version I did not yet implemented the intersection logic as it will require a bit more work, but the current state of my command is already rather satisfying. I will ultimately add a switch to let the user control whether partially selected components have to be included or not in the selection.
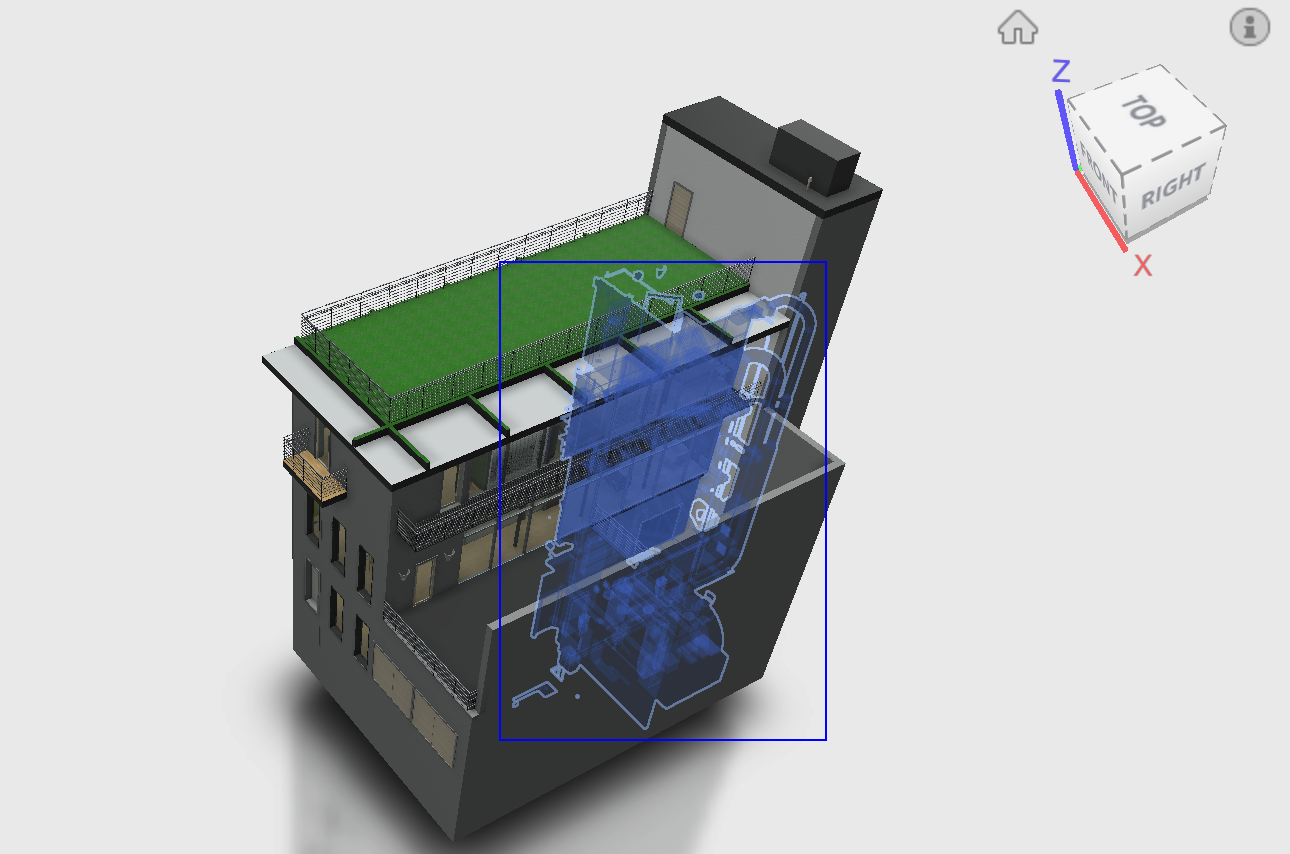
The command also supports working with multiple models in the same scene. It currently performs detection on a single model at a time for performance reasons but could easily be extended to scan all models in the scene if needed.
You can see below a recording where I am testing the selection in a scene containing three models, including our Toronto office with a non-trivial number of components. The performance of the selection is quite acceptable on my machine.
Live version is available for you to play with here and the selection logic code is below: