In the previous post, "Move viewer's camera to rooms," we discussed how to utilize a third-party library, tween.js, to create tween points from the current camera position to the center of the room's bounding box.
You may wonder how to replicate a similar action on an object in the viewer. It's easy to migrate the code and change the target from a room to an object.
However, you may notice that the camera animation in the demo video of the post appears to be shaking. To improve behavior, we will introduce a new algorithm to replace tween.js.
Then let's see how it works below!
Best Viewpoint Candidate Sampling Algorithm
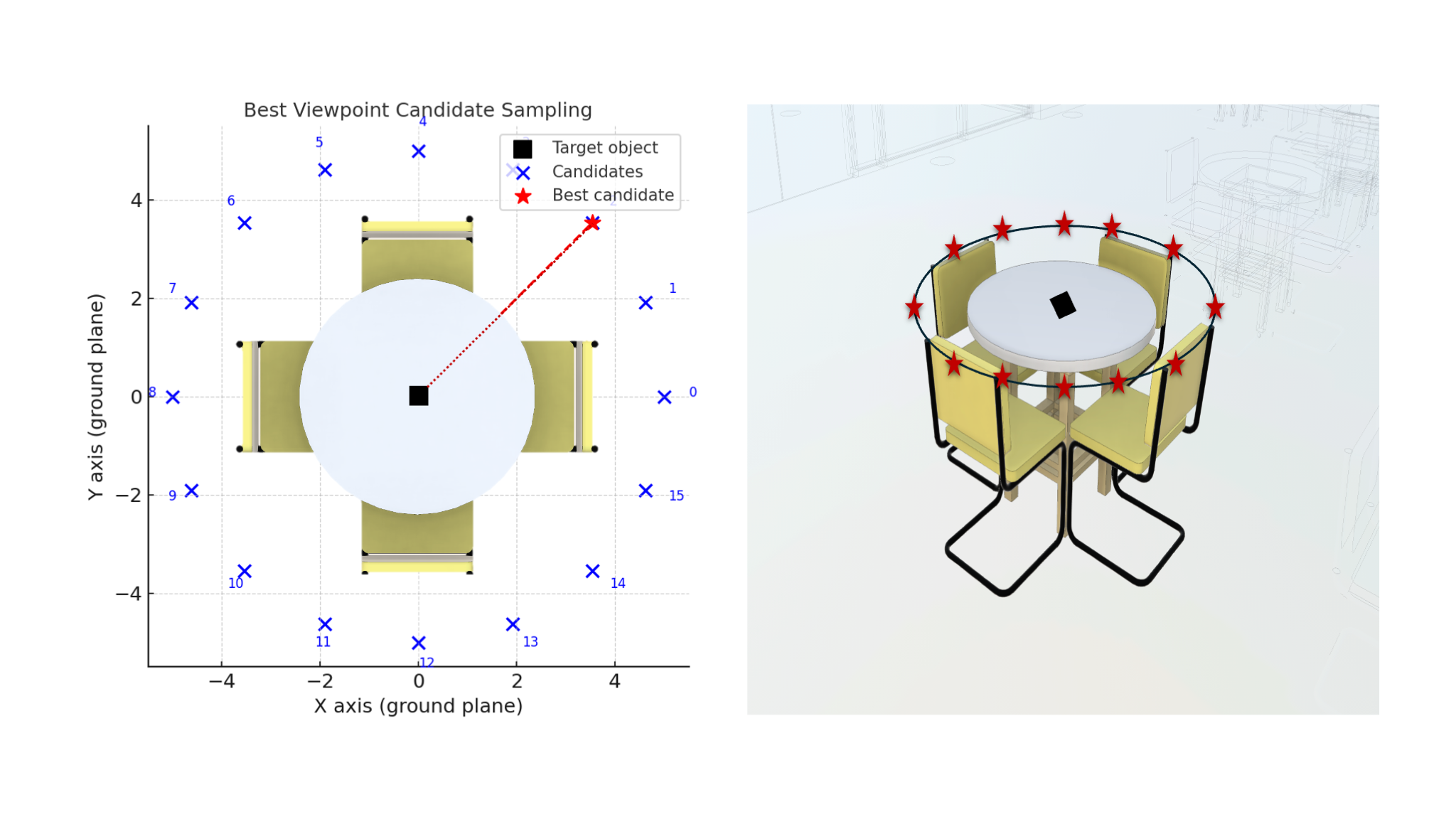
To achieve the goal of not using a third-party library, we introduce an algorithm that leverages the bounding boxes and ray casting to attempt to find the optimal viewpoint by calculating camera view candidates rather than creating tween points. Here are the main ideas of this algorithm:
1. Target Preparation
- Computes the bounding box of the target objects. We build our own AABB Octree for spatial indexing.
- Extracts key points (corners, face centers, center) from the target's bounding box for visibility analysis.
2. Candidate viewpoints
- Samples a set of candidate camera positions around the object (like walking around it) in a hemisphere.
- For better view angles, it skips edge-on angles if the object is elongated and samples in a horizontal direction.
- As the above diagram shows, we divide the hemisphere into parts as the candidate camera positions (eyes).
3. Visibility evaluation
- From each candidate's eye, casts rays to key points.
- Counts how many keypoints are visible (not blocked by other objects).
- Collects blocker dbIds along rays that intersect before hitting the target.
4. Scoring
- To find the best viewing point, we use this formula to calculate the score for each candidate. Score = visibility – blockers – inside penalty.
- Chooses the highest-scoring candidate as the best view.
5. Result
- Best candidate view is applied (or previewed with blockers colored).
Demo
Here is the code snippet of the core function:
/**
* Core computation engine that finds the optimal viewing angle for given objects.
*
* Algorithm overview:
* 1. Generates candidate camera positions in a ring around the target
* 2. Filters candidates based on geometric heuristics (elongation analysis)
* 3. Evaluates each candidate using visibility and blocker analysis
* 4. Scores candidates based on weighted visibility and blocker penalties
* 5. Returns the highest-scoring candidate as the best view
*
* @async
* @param {number|number[]} dbIds - Viewer dbIds of target objects
* @param {Object} [userOpts={}] - Options to override default settings
* @returns {Promise<Object>} Result containing best candidate and all evaluated candidates
* @returns {Object} result.best - Highest scoring candidate with position, target, score, and blocker info
* @returns {Array<Object>} result.candidates - All evaluated candidates with detailed scoring data
*
* @example
* const result = await extension.computeForBestView([123, 456], {
* numCandidatesRing: 24,
* weightVisible: 0.7,
* weightBlockers: 0.3
* });
*
* console.log(`Best view score: ${result.best.score.toFixed(3)}`);
* console.log(`Visibility: ${(result.best.visibleFrac * 100).toFixed(1)}%`);
*/
async computeForBestView(dbIds, userOpts = {}) {
const opts = Object.assign({}, this.opts, userOpts);
const viewer = this.viewer;
const model = viewer.model;
const ids = Array.isArray(dbIds) ? dbIds : [dbIds];
await ensureInstanceTreeReady(model);
// Target box & keypoints
const targetBox = await getWorldBBoxForDbIds(model, ids);
const targetCenter = targetBox.getCenter(new THREE.Vector3());
const keyPoints = bboxKeyPoints(targetBox);
// AABB fragment cache (for fallback + “inside-other”)
const { allFrags, targetFragSet } = buildFragmentBboxCache(model, ids);
let accel = null;
if (opts.useOctree) {
const worldBox = safeModelBoundingBox(model);
accel = buildAabbOctree(allFrags.nonTarget, worldBox, { maxItemsPerNode: opts.maxItemsPerNode, maxDepth: opts.maxDepth });
} else {
accel = allFrags.nonTarget; // flat array
}
const aabbItems = opts.useOctree ? flattenOctreeLeaves(accel) : accel;
// Make sure perspective is on for consistent computeFit
const nav = viewer.navigation;
if (!nav.getCamera().isPerspective) nav.toPerspective();
const camera = nav.getCamera();
const fov = nav.getVerticalFov();
const aspect = camera.aspect;
// Ring directions (XZ plane)
const camDir = new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, -1).applyQuaternion(camera.quaternion).normalize();
// World axes for narrow-side heuristic
const worldRight = nav.getWorldRightVector().clone().normalize();
const worldUp = nav.getWorldUpVector().clone().normalize();
const worldFront = new THREE.Vector3().crossVectors(worldUp, worldRight).normalize();
// Elongation analysis
const size = targetBox.getSize(new THREE.Vector3());
const spanRight = Math.abs(size.clone().multiply(worldRight).length());
const spanFront = Math.abs(size.clone().multiply(worldFront).length());
const wideSpan = Math.max(spanRight, spanFront);
const narrowSpan = Math.max(1e-6, Math.min(spanRight, spanFront));
const elongated = opts.enableNarrowSideSkip && (wideSpan / narrowSpan) > opts.coverageFactor;
const wideAxis = elongated ? (wideSpan === spanRight ? worldRight : worldFront) : null;
const ringDirs = [];
for (let i = 0; i < opts.numCandidatesRing; i++) {
const theta = (i / opts.numCandidatesRing) * Math.PI * 2;
ringDirs.push(new THREE.Vector3(Math.cos(theta), -Math.sin(theta), 0).normalize());
}
const filteredDirs = opts.preferFrontHemisphere ? ringDirs.filter(d => d.dot(camDir) < 0) : ringDirs;
// Build candidates using computeFit + pull-back + height clamp
const candidates = [];
for (const d of filteredDirs) {
const seedEye = targetCenter.clone().add(d);
let eye;
if (nav.computeFit) {
const fit = nav.computeFit(seedEye, targetCenter, fov, targetBox, aspect);
eye = fit && fit.position ? fit.position.clone()
: targetCenter.clone().add(d.clone().multiplyScalar(suggestedDistanceFor(targetBox, camera, 1.6)));
} else {
eye = targetCenter.clone().add(d.clone().multiplyScalar(suggestedDistanceFor(targetBox, camera, 1.6)));
}
const delta = eye.clone().sub(targetCenter);
eye.add(delta.clone().multiplyScalar(opts.bumpBackPct));
eye.z = Math.max(eye.z, targetCenter.z);
if (wideAxis) {
const bearing = delta.clone().normalize();
const angDeg = Math.acos(THREE.MathUtils.clamp(bearing.dot(wideAxis), -1, 1)) * 180 / Math.PI;
if (Math.abs(angDeg) < opts.ignoreNarrowSideDeg) continue;
}
candidates.push({ eye });
}
if (!candidates.length) {
const dist = suggestedDistanceFor(targetBox, camera, 1.6);
const eye = targetCenter.clone().add(camDir.clone().multiplyScalar(-dist));
eye.z = Math.max(eye.z, targetCenter.z);
candidates.push({ eye });
}
// Geometry or AABB fallback?
const useGeometry = allGeometryReady(viewer) && !!viewer.impl?.rayIntersect;
// Evaluate
let best = null, bestScore = -Infinity;
const results = [];
for (let i = 0; i < candidates.length; i++) {
const eye = candidates[i].eye;
const visibleFrac = useGeometry
? visibilityFractionByRayOcclusionGeometry(viewer, eye, targetCenter, keyPoints, ids, opts.samplePerPoint)
: (opts.useOctree
? visibilityFractionByRayOcclusion(eye, targetCenter, keyPoints, accel, targetFragSet, opts.samplePerPoint)
: visibilityFractionByRayOcclusionFlat(eye, targetCenter, keyPoints, accel, targetFragSet, opts.samplePerPoint));
const blockers = useGeometry
? gatherOccludersForViewWithCounts_Geometry(viewer, eye, keyPoints, ids, {
occluderMode: opts.occluderMode, occluderK: opts.occluderK, minRayHits: opts.minRayHits, maxOccluders: opts.maxOccluders
})
: (opts.useOctree
? gatherOccludersForViewWithCounts_Octree(eye, keyPoints, accel, targetFragSet, {
occluderMode: opts.occluderMode, occluderK: opts.occluderK, minRayHits: opts.minRayHits, maxOccluders: opts.maxOccluders
})
: gatherOccludersForViewWithCounts_Flat(eye, keyPoints, accel, targetFragSet, {
occluderMode: opts.occluderMode, occluderK: opts.occluderK, minRayHits: opts.minRayHits, maxOccluders: opts.maxOccluders
}));
const blockerCount = blockers.dbIds.length;
const normBlockers = blockerCount / Math.max(1, keyPoints.length);
const insideOther = isEyeInsideAnyAabb(eye, aabbItems, targetFragSet);
const score = (opts.weightVisible * visibleFrac)
- (opts.weightBlockers * normBlockers)
- (insideOther ? opts.insidePenalty : 0);
const cand = {
index: i,
position: eye.clone(),
target: targetCenter.clone(),
visibleFrac,
score,
insideOther,
blockers
};
results.push(cand);
if (score > bestScore) { bestScore = score; best = cand; }
}
return { best, candidates: results };
}
And a small example of calling an extension function directly
// After loading Viewer & model(s)
const ext = await viewer.loadExtension('Autodesk.DeveloperAdvocacySupport.HumanEyeBestViewExtension', {
// optional overrides:
numCandidatesRing: 20,
preferFrontHemisphere: true,
enableNarrowSideSkip: true,
weightVisible: 0.6,
weightBlockers: 0.4,
applyView: true
});
// Run on selection via toolbar button, or programmatically:
const sel = viewer.getSelection();
const result = await ext.computeForBestView(sel.length ? sel : [YOUR_DBID]);
console.log('Best view:', result.best);
ext.apply(result.best);
And here is the complete code sample. Hope you enjoy it!
https://gist.github.com/yiskang/f7c116e445e15a9c027b821064454d6b
If you have any questions or feedback, please don't hesitate to contact us through our APS support channel.